|
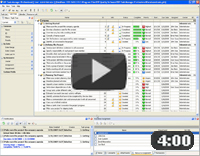
Task Management Software |
 |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
 TESTIMONIALS TESTIMONIALS
|
|
"...This is an excellent program. I'm so glad that I stumbled on to this when researching for task management programs. Very low learning curv, quite flexible, and the price is right. Tried at least 20 other programs, either too complicated, too expensive, or poor documentation..."
Chad Lindsey -
Honolulu, HI
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
First aid checklist |
|
|
|
|
|
|

 |
This first aid checklist explains the general approaches for those who aren’t professional medics. This is not a manual, so it doesn’t contain profound answers on how you can relieve different diseases and solve sudden problems with health, as this is quite vast and serious topic, but instead of specifics, this checklist is about making you a more prepared person in this area as it explains basics you need to know, and a number of serious mistakes you should avoid categorically.
|
| Order 750 checklists in MS Word and PDF printable format at $49.99 USD only. |
BUY NOW!  |
First aid basics:
- In order of being able to provide simplest kinds of help to injured people you need to master the following procedures and skills: quick health problems diagnostics, treatment of burns, stopping bleeding, treatment of broken bones, making CPR, giving injections, treatment of common illness, absorbing poisons, etc.
- Any person can take a course of trainings to be sure he will know what to do in a case of some emergency situation when someone nearby would need an immediate first aid. Usually such courses are learnt in schools and other popular educational institutions (as part of their main educational program or as an elective course), and in certain volunteer organizations.
- Enterprises where employees are engaged into potentially dangerous kinds of working activities normally provide their workers with special information and trainings related to their job specificity, so employees are taught to react properly to typical injuries and emergencies.
- If you are not properly qualified to provide first aid (you weren’t at least minimally taught on how to provide basic medical help), then the best thing you can ever do is to instantly call for a professional help (immediately call to emergency and ask for urgent help from local ER).
- The main way to avoid need in first aid is precaution, so you should be highly attentive to general safety requirements and rules at any place where you are. Different public places where you can be at may have their own instructions explaining how to avoid and remedy the most common accidents related to local specificity (for example in summer camps and on the beaches the rules can be about water safety, preventing sunburns, etc).
- When a person is lying unconsciousness after some serious accident (for example a car accident), you shouldn’t move him anyhow and shouldn’t put any objects under his head, or do any other unprofessional operations with his body, you should wait until medics arrive, because you can never definitely know what internal injuries were caused and how to treat them – sometimes moving or touching the victim may worsen the situation, or even kill him.
- Medical institutions usually publish different professionally-composed worksheets on their web-sites. These worksheets created by professional physicians explain laymen how to react in different cases (burns, broken bones, asthma, chest pains, etc). You need to study these professional checklists to know how to act in order of providing first aids to victims of different accidents (or at least to learn what actions would be completely wrong). Anyway, it is completely useful to eliminate some dangerous misconceptions in your mind (to know some of them you can look through the last section of this checklist).
Well-stocked first aid kit contains the following items:
- Comprehensive handbook;
- Antiseptic creams, ointments and wipes;
- Bandages and gauze of various kinds and sizes;
- Tweezers, scissors, and knife;
- Sterile wipes;
- Syringes;
- Iodine and medical cotton;
- Rinse solutions;
- Court plaster;
- Antibiotic;
- Anti-diarrhea medicine;
- Purgative;
- Analgetic medicine;
- Antihistamine;
- Absorbent carbon;
- Cough drops (syrup);
- Cold/Flu tablets;
- Decongestant;
- Vitamins;
- Nasal spray;
- Insect repellent;
- Antacid tablets;
- Prescription medicines;
- Sunburn relief spray;
- Foot powder;
- Magnifying glass;
- Thermometer;
- Adhesive tape;
- Small mirror;
- Eye drops and eyedropper;
Some situations when a person needs appropriate first aid steps (while being unconsciousness or confused):
- Diabetes;
- Heat stress;
- Injury due to some accident;
- Seizures;
- Alcohol or drug intoxication;
- Poisoning with chemicals;
- Overdose;
- Heart attack;
- Choking;
- Dehydration;
- Asthma;
- Illness or infection;
- Drowning;
Some of the most common mistakes and misconceptions:
- Never treat a burn with butter or anything else that has not been recommended by a pharmacist or physician. Any burn where the skin is damaged should be immediately shown to a medic.
- Be absolutely careful when using tourniquets to stop bleeding. This is a way to control bleeding and it can be used only in very severe cases, because tourniquet misusing can easily lead to gangrene (death of tissue) as it completely blocks blood flowing to the limb. When tourniquet is used it should be loosened every few minutes to allow some blood flowing through.
- Don’t suck a snake bite to extract the venom as it is shown in old “cowboy movies” – this attempt doesn’t work as venom goes into body very quickly with the blood stream. Besides this, even if some venom can get into your mouth, you will get poisoned as well.
- When a person suffers from convulsions or seizure you shouldn’t put any objects into his mouth “to prevent him from biting his tongue”. These objects can hurt the person’s mouth and teeth, can get broken and lead to choking, and these things could happen rather than he can bite his tongue.
- When a person is impaled, don’t try to remove the object from the body, as this could cause further internal damage or increase the risk of severe bleeding, so you need better to stabilize the object and instantly call emergency (or if possible immediately go to local ER).
- When person is poisoned, one of the most common misconceptions is to induce vomiting. Corrosive poisons burn the esophagus on the way down, and if the victim vomits, the poison will now burn it on the way up, besides this, the poison may now be inhaled by the lungs, damaging them very easily.
- The same is about drinking water or milk to “absorb poison” in your stomach – this won’t help, but could lead to further problems as water can make a reaction with some chemicals. Immediately call poison control service or emergency, and bring the ingested substance with its container to the local ER (or be ready to show it when medics arrive).
- Don’t fail to get immediate medical help after an electric jolt (from lightning, a power line, or home electrical cords), as even if a victim looks ok, and electrical burns are not evident, there can be invisible and serious injury deeper inside the body.
- It is strongly inadvisable to move a victim injured in a car accident out of the vehicle until paramedics arrive. A person with a spinal-cord injury will not necessary look badly injured, but pulling a victim out of his vehicle (or even removing helmet from an injured motorcyclist) could lead to paralysis or death.
- Don’t rub frostbites (frozen skin/tissue) to warm up them up. When water in the tissue freezes, because of frostbite, it expands and forms tiny crystals in the skin cells, so that rubbing the skin can cause these tiny water crystals to make small cuts in the skin from the inside. The best you can do is to warm up those body parts by going into a warm premise, or placing them on another body part that is warm.
| Order 750 checklists in MS Word and PDF printable format at $49.99 USD only. |
BUY NOW!  |
|





 |
CentriQS Tasks Management Solution 
Looking for multi-user task management software? Try CentriQS complete task management solution for planning, tracking and reporting tasks, projects, and schedules. Increase productivity of your small business or office by better organizing your employees' tasks and time.
 FREE Download CentriQS FREE Download CentriQS
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CentriQS  -15% OFF -15% OFF |
All-in-one business management software
for small and midsize enterprises |
 |
|
|
| VIP Task Manager |
Multi-user project management software
to plan, schedule and track project tasks. |
 |
|
|
| VIP Checklists
|
More than 750 ready-to-use to-do lists
to plan your personal and business life |
 |
|
|
| VIP Team To Do List |
Professional task management software
to make and send team todo lists by email |
 |
|
|
| VIP Organizer |
Personal time management software
to organize time at home and at work |
 |
|
|
| VIP Simple To Do List
|
Simple and effective to-do list software
to plan daily chores, trips, wedding, etc. |
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|